European Buckthorn
 Rhamnus cathartica
Rhamnus cathartica
Common Buckthorn can lead to significant yield losses and lowered grades of cereal by being an alternate host for a fungus that causes oat rust. It is often confused with Chokecherry.
Â
Â
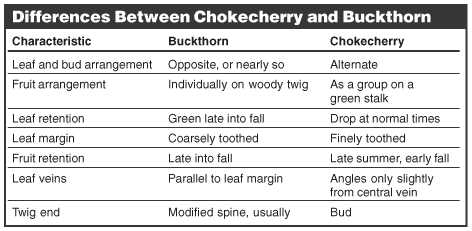
*graphic courtesy of the University of North Dakota
Origin
European Buckthorn is native of Eurasia. It was introduced to North America as an ornamental shrub, for fence rows and wildlife habitat.
Status
This plant is found in Manitoba and is a large problem in natural areas within Winnipeg.
Impacts
This plant is able to successfully invade habitats because of its tolerance of a wide range of moisture and light conditions, and its heavy seed production.
The dense shade produced by stands often reduces biodiversity in a habitat. Thorns can be harmful to humans or animals that come into contact.
Where to Look
Common in fence rows, pastures, roadsides, woodland and abandoned areas. It can also be seen infesting natural areas and invading river bottom and upland forest habitat.
Identification
Leaves: Dark green with slightly serrated edges, elliptic to ovate, 3.5 - 7.5cm. They grow in pairs, but not exactly opposite.
Flowers: Small, greenish to yellowish, short-stalked and in small clusters.
General: Shrub to 6m tall, outer bark is dark with small pores and inner bark is orange.
Resources
European Buckthorn ISCM Fact Sheet
2011 Rural Municipality Distribution Map
2010 Rural Municipality Distribution Map.
European Buckthorn MWSA 2009 Survey Map
Common Buckthorn and Glossy Buckthorn — Project Fact Sheet
Â
Back to Terrestrial Invasive Species List
Â
© Copyright 2004-2025 - CMS Made Simple
This site is powered by CMS Made Simple version 1.4.1


